A Plant Ability to Survive Underground and Then Able to Sprought Again in Sprig
Abstract
Plants regularly confront dry conditions. Not having enough water poses a serious threat to a plant's ability to abound and develop or fifty-fifty merely survive! If plants die, we will not have enough food to swallow! How do plants manage to survive during water shortages? They must somehow be able to sense, respond, and arrange to changes in water availability. They exercise this through a range of techniques that allow for a institute to gainsay h2o shortages. A plant's structural "armor" helps it to decrease the amount of h2o it loses to the environs and increment h2o storage. Plants respond to water shortages in very complex ways. These responses can include changes in the plants' growth and in their ability to protect themselves confronting toxic chemicals that accumulate in the plant during dry periods. All of a plant's responses are straight controlled by the institute's genes. If we can understand the genes that are involved in protecting plants against drought, in the time to come we might be able to make genetically modified crops that can tolerate global warming and climate changes.
Have you heard people speaking about global warming and climatic change? Do yous know what these terms mean? These terms basically imply that the earth is getting hotter every year. These higher temperatures pb to unexpected and unusual weather patterns. I of these extreme weather condition patterns is frequent and severe droughts. Droughts are very long dry out periods without any rain. What practise severe droughts mean for plants? Well, plants are sessile , which means they stay in 1 place and can't move around like nosotros can. They can't pull upward their roots and relocate to a shady or damp spot. Therefore, plants somehow need to deal with these ever-increasing drought conditions, or they will simply die. Remember, plants are our food. We swallow plants raw or cooked (those vegetables your mom insists y'all eat!) or processed, similar your favorite box of breakfast cereal [which is fabricated from wheat or maize (corn)]. And so, if plants die considering of droughts, we will non have enough food to eat!
If there is no water around, what tin can plants do to survive? Amazingly, all plants seem to accept a number of genes for drought-defense strategies encoded in their Deoxyribonucleic acid. Genes are small sections of Dna, like chapters in a volume. How they utilise these genes determines their ability to survive drought.
Some plants are drought-resistant. When we talk about drought-resistant plants, we hateful plants that can withstand dry weather condition without dying. A drought-resistant plant can survive drought by using three defense strategies: escaping, avoiding or tolerating the loss of water [one]. Drought tolerant plants are quite rare in nature and can endure long periods with no h2o at all. Some of the well-nigh spectacular drought tolerant plants are called resurrection plants. Resurrection plants are able to survive long periods (up to three years!) without any water. Yet, give them a little water and they will spring back to life in a twenty-four hour period or 2. Other drought-resistant plants may not be every bit spectacular, merely they too can survive brusk periods of drought using special techniques and defense strategies.
Some Plants Take Special Structures That Help Them to Survive in Drought Weather condition
Some plants are able to survive droughts because of their unique structures. These structural features include the external armor of plants that protects them against water loss, as well as tools to help the plants absorb and store h2o. Drought-resistant plants tin can be especially adapted to alive and survive in very dry environments. These plants often wait quite dissimilar from plants living in areas where water is easily available. The drought-resistant plants normally accept special "abstention" (1 of the defense adaptations!) features to make sure less water is lost to the environment or that more than water gets absorbed and stored in the plant. Plants chosen desert succulents are a practiced instance of plants that have drought avoidance strategies [2]. Desert succulents take thick fleshy leaves, which often don't resemble leaves at all, and they take a thick waxy layer to foreclose water loss. Desert succulents also take all-encompassing root systems that search for h2o under the dry desert soil (Figure one). Some succulents have specialized roots that form large bulb structures, which are really underground water reservoirs for the found. These plants can survive years of drought using the h2o stored in their bulbs.
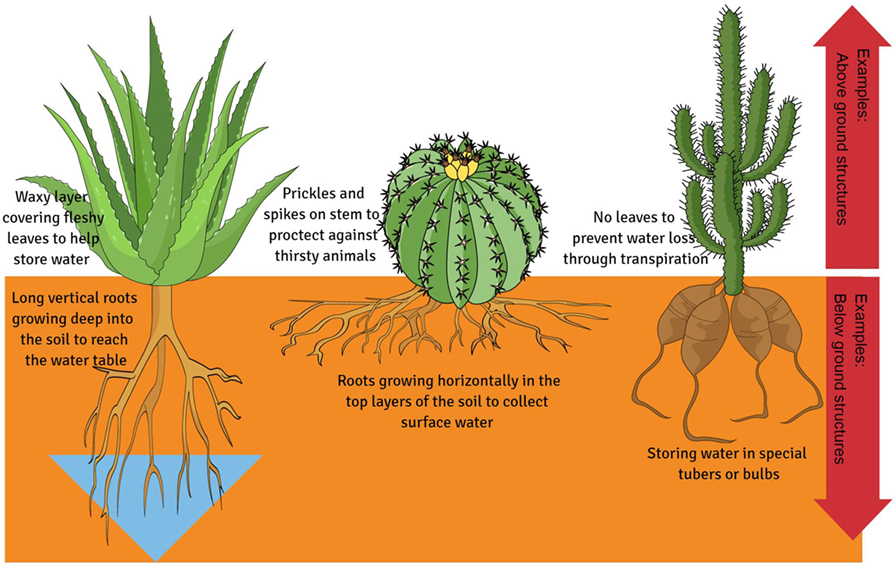
- Figure 1 - Extreme structural adaptations found in plants to combat water loss and store more than water.
Most of the water a establish loses is lost due to a natural process called transpiration . Plants have little pores (holes or openings) on the underside of their leaves, called stomata . Plants will blot water through their roots and release water as vapor into the air through these stomata. To survive in drought conditions, plants need to decrease transpiration to limit their water loss. Some plants that alive in dry out conditions accept evolved to have smaller leaves and therefore fewer stomata. Farthermost examples are plants with leaves that resemble spiky thorns. Some plants may too completely shed their leaves in a drought, to forbid water loss. The basic rule is that fewer leaves hateful less h2o loss through transpiration. These extreme leaf adaptations can also protect the plants from hungry and thirsty birds and animals (Figure 1). You certainly would non like to have a prickly meal!
Some adaptations are quite clever and involve plants "escaping" drought every bit seeds (call back, escape is another defense strategy). The seeds survive during the dry spells and very quickly germinate (sprout), grow and produce more seeds when rains autumn. These seeds are and then scattered and tin besides survive extreme harsh conditions for long periods of time. Looking closely at desert soils, y'all volition discover a lot of seeds lying around, just waiting for rain before germinating again.
Some Plants also Have Internal Defenses Confronting Drought
In addition to special structures, plants have internal defenses to protect them against water shortage, as well. When a plant experiences drought weather, some reactions volition quickly happen inside the institute to aid the constitute with the stress of the drought. These reactions that occur in the plant are often quite complex and sophisticated. We volition give yous some examples.
Plants Yet Need to Perform Photosynthesis During Drought
Plants are dark-green considering they contain a light-green chemical called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is packed into special structures called chloroplasts, which are the energy factories of plants. Together with water and carbon dioxide (CO2), chlorophyll uses sunlight to create sugars. These sugars allow the constitute to abound and flourish. This is the procedure of photosynthesis and it is linked to the availability of water.
When there is not a lot of water in the constitute's soil, the process of photosynthesis volition happen a little differently and will result in the build-upwards of damaging chemicals called free radicals . This means that plants need to carefully control how they use the energy of the sun. During photosynthesis, COii must enter the establish through its stomata (the niggling pores mentioned earlier). Merely remember, open stomata mean that water will be lost through transpiration! So, the plant is faced with the difficult problem of making sure it has enough water and also enough CO2 for photosynthesis to occur. To do this, plants use a "director" called abscisic acid ( ABA ).
When a plant experiences a shortage of water, ABA is rapidly produced and transported to the stomata. In the stomata, ABA controls how the stomata open up and close by manipulating something called turgor force per unit area (Figure 2) [3]. Turgor pressure is the pressure applied on the wall of the plant cell by the fluids inside the prison cell. The more water is in the cell (the fuller the cell) and the bigger the pressure. Management of turgor pressure provides a balance between CO2 intake and h2o loss, so that photosynthesis can occur. But, if water remains limited in drought conditions, eventually the plant will be unable to cope with the stress of the drought and the entire photosynthetic process can stop working properly. Notwithstanding, drought-resistant plants have figured out a clever way to avoid the trouble of losing water during photosynthesis. They only open up their stomata during the cool of the dark to take up CO2. They then store this COtwo and use information technology in the daytime for photosynthesis. This manner, they lose less water during the day because they tin keep the stomata airtight, but they tin can keep to grow—although a petty slower than normal.
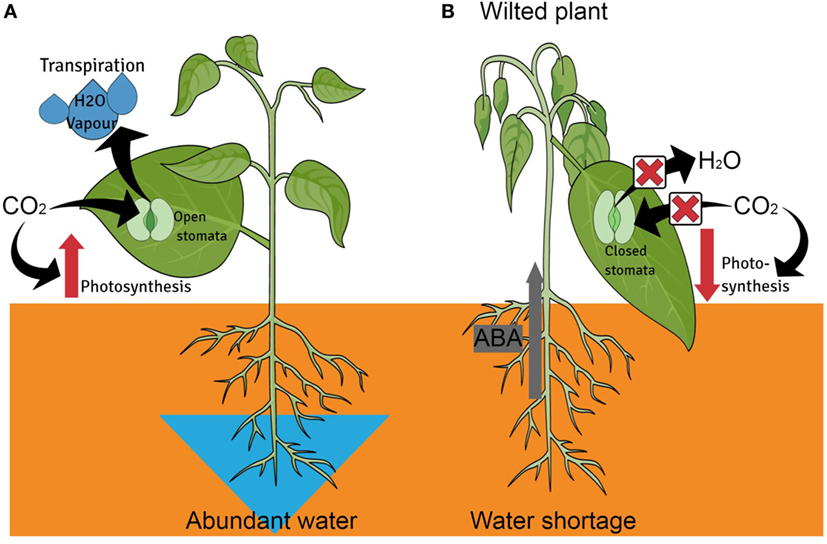
- Figure 2 - Internal defenses of plants under water stress.
- (A). When plenty of water is bachelor in the soil, plants will blot h2o through its roots. This water will be used by the plant or released through transpiration by open stomata in the leaves. Photosynthesis will also occur normally with COtwo and oxygen being absorbed and released through the open stomata. (B). But when limited water is available in the soil, plants effort to prevent water loss. Water loss through transpiration tin be reduced by closing the stomata in the leaves using a substance called ABA. When the stomata is closed photosynthesis will decrease because no CO2 tin enter through the closed stomata. Less photosynthesis means less energy is produced by the plant and the constitute stops growing.
Plants Need to Protect Themselves from Dangerous Free Radicals
In drought conditions when a plant cannot seem to balance photosynthesis and water loss properly, the plant will have to deal with nasty little molecules chosen complimentary radicals. Free radicals occur naturally during photosynthesis, merely when in that location isn't a lot of h2o available more than free radicals form. Free radicals can be very dangerous for the cell, because they tin cause damage to Dna, cell membranes, proteins, and sugars (all of these substances are essential for a cell'due south survival)!
Plants are used to dealing with depression amounts of free radicals. However, drought tolerant plants are really practiced at dealing with free radicals, considering they accrue protective substances. These protective substances are called costless radical scavengers. The presence of gratuitous radical scavengers often causes a change in the color of the establish. Plants often turn red or purple when these scavengers accrue (do y'all see the purple leaves of the dry plant in Figure 3B?). The costless radical scavengers occur widely in nature and are very good at mopping up complimentary radicals to protect plants from their harmful effects.
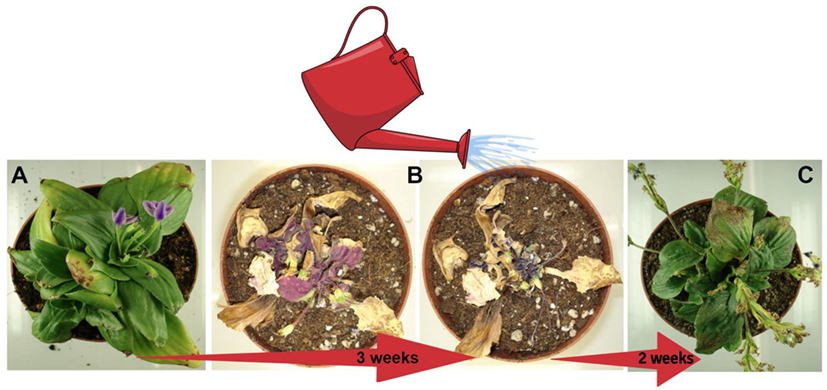
- Figure iii - The resurrection plant, Craterostigma pumilum.
- (A). This is how the plant looks when information technology is growing in conditions where plenty water is bachelor. (B). The two middle pictures show the plant when no h2o is available, after 3 weeks without water. Doesn't information technology look dead to you? (C). If the aforementioned dry out, dead-looking plant is watered, inside 2 weeks the plant will recover from the drought and start producing seeds.
Plants Need to Control the Amount of Water within Their Cells
Osmosis is an important concept in biology. Basically, osmosis is the move of h2o beyond a membrane (like a cell membrane) to an expanse where certain molecules (like salts, sugars, and free radicals) occur in college concentrations. By doing then, the water will dilute the concentration of these molecules and then that the concentration is equal on both sides of the membrane. At present think almost what happens to a plant that is suffering from the loss of water. At that place is non plenty water to allow osmosis to occur, and so molecules become super full-bodied inside the plant cells. This is generally non a skillful affair, especially if these molecules are gratis radicals.
Once more, drought tolerant plants accept some very cool strategies to fight this trouble. At the offset signs of drought, the cells of these plants volition accumulate a bunch of molecules involved in what is called osmotic adjustment (OA) [3]. OA is the alter is solute concentration in a cell. This is similar when yous dissolve carbohydrate in water, where saccharide is the solute. These molecules (solutes) tin exist sugars, amino acids or small proteins. The purpose of these molecules is to limit the movement of h2o out of the cell. What makes these OA molecules unique in drought tolerance is that they serve many functions. The OA molecules can physically bind to DNA and proteins to protect them from free radicals. They can also bind water itself, preventing it from moving out of the constitute cells. These OA molecules besides bind to membranes, stabilizing the structure of the institute when h2o is restricted.
Resurrection plants are perfect examples of how drought tolerant plants bring together the concepts we've discussed so far. Resurrection plants are able to survive complete loss of water. They accumulate vast quantities of OAs, release free radical scavengers and produce special protective proteins to survive long and severe droughts. They do all of this while they also fold their leaves abroad and wait until rain falls (Figure 3). The process can be compared to bears going into hibernation.
A Establish's Genes Control its Responses to Drought
Keep in heed that we take discussed these processes used to protect plants from drought in a very simplified way. Looking closely at these processes is actually very complicated. At the very basic level, these processes are regulated by the plant's use of its genetic code—its genes. Substances necessary to survive drought will be produced by accessing this code at the right time. This accessing of the genetic code to assist a plant survive a drought is chosen the genetic response of the establish.
The genetic responses of a establish experiencing the stress of a drought are very complex—lots of genes are switched on or off. Using advanced computer technologies, scientists are now able to identify virtually of the genes that play a role in protecting a found from drought. This applied science has found that literally hundreds of genes are switched on and off, depending on where and when they are needed! We tin't listing all of these genes, because you will be completely bored at the end of the first page! What we will say is that these genes autumn mainly into three groups: (ane) genes that control other genes important for switching genes on and off; (ii) genes that produce substances that help with drought protection in the plant; and (3) genes involved in water uptake and send.
Why practice y'all recall information technology might be of import to know which genes play a role in helping plants avoid or tolerate drought? Most of our crops are actually non able to survive droughts. How are nosotros going to protect our crops or brand them more resistant to these droughts? We need to use the knowledge of the genes that are turned on or off during drought atmospheric condition to produce plants that are more resistant to drought.
Over the years, found scientists have had some success in producing drought-resistant crops. These drought-resistant crops were produced mainly by selecting and convenance private plants that survived well under drought atmospheric condition. Over the past few decades, scientists working on genetically modified (GM) plants also started to focus on producing drought-resistant crops [4].
To produce a GM plant, a new gene (from whatsoever source!) is inserted into the Dna of the plant. Past inserting this new cistron/due south, the scientist hopes to introduce a new, useful trait into the GM institute. Imagine existence able to choose from hundreds of helpful genes in a resurrection plant and introduce some of them into wheat! Unfortunately, only a handful of GM drought-resistant plants (such every bit maize/corn and sugarcane) have been successfully produced. Much more work needs to be done, including disarming the general public that GM plants are non unsafe!
Conclusion
Plants are really vulnerable when information technology comes to h2o scarcity. Drought will influence a plant's growth, development, productivity and ultimately its survival. All the same, plants do have some built-in protection against drought. They can have some structural adaptations to avert or tolerate aridity. They also accept some internal defenses that are activated to effort to limit water loss when they realize water is condign deficient. All of these defense systems are regulated by the plant's genes. Noesis of these genes and how they are involved in protecting the plant against drought provide humankind with a promise to make drought-resistant GM crops.
Glossary
Sessile: ↑ An organism that can't move and stays in one place, similar a found.
Succulents: ↑ Plants that take thickened and fleshy leaves and stems, in which water can be stored.
Transpiration: ↑ The procedure where plant roots will take upward water and and then release h2o vapor through pores (stomata) in the leaves.
Stomata: ↑ Little holes in the lower surface of a leaf through which h2o and gas tin can move in and out of a plant.
Photosynthesis: ↑ The process where plants use water, light and CO2 to produce their ain food (in the class of sugars) and release oxygen into the air.
Costless radicals: ↑ Molecules that volition react with, and damage, anything they come in contact with.
ABA: ↑ A plant hormone called abscisic acrid that helps take intendance of the water rest in plants.
Turgor pressure: ↑ The tension exerted on a plant cell wall by the fluids inside the jail cell. Imagine filling a airship you've placed within a glass jar. As y'all fill the balloon more, it presses upward against the rigid glass jar merely like the fluids against the rigid found prison cell wall.
Osmosis: ↑ Moving water through a cell membrane from one cell to the next cell. Why? To ensure equal concentrations of solutes on both sides of the membrane.
Osmotic adjustment: ↑ Changing the concentration of solutes in a constitute cell.
Solute: ↑ The substance (like sugar) you are dissolving in a solution (similar water).
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
Figures were created in the Mind the Graph platform (world wide web.mindthegraph.com).
References
[1] ↑ Basu, S., Ramegowda, V., Kumar, A., and Pereira, A. 2016. Plant adaptation to drought stress. F1000Res 5(F1000 Faculty Rev):1554. doi:x.12688/f1000research.7678.ane
[2] ↑ Dimmitt, M. A. 1997. How plants cope with the desert climate. Sonorensis. Vol. 17. Available at: http://www.desertmuseum.org/programs/succulents_adaptation.php
[3] ↑ Osakabe, Y., Osakabe, K., Shinozaki, One thousand., and Lam-Son, T. 2014. Response of plants to water stress. Front end. Plant Sci. v(86):1–8. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00086
[4] ↑ Blum, A. 2014. Genomics for drought resistance – getting down to earth. Funct. Constitute Biol. 41:1191–8. doi:10.1071/FP14018
Source: https://kids.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frym.2017.00058
0 Response to "A Plant Ability to Survive Underground and Then Able to Sprought Again in Sprig"
Post a Comment